For those who are not aware, a content delivery network (CDN) is basically a group of servers distributed across various geographical locations. They work together to provide quick delivery of content on the internet to internet users at various locations.
CDNs usually allow for quick transfer of assets required for loading content on the internet. Among them are JavaScript files, HTML pages, videos, images and other required content. Their services are popular and are growing as they serve the vast majority of internet traffic today. Amazon, ESPN, Facebook, Netflix and the like are major examples.
A well-configured CDN can help protect websites against some common and foul online attacks, especially against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
What makes a content delivery network different from a typical web host?
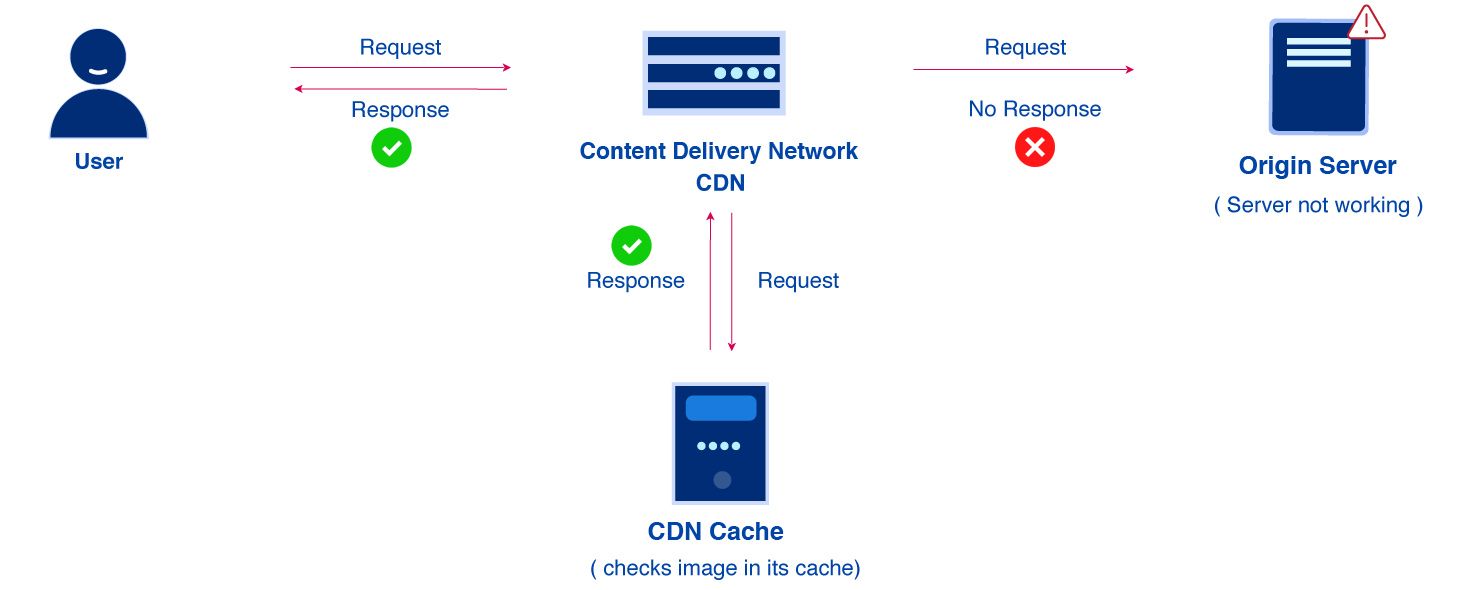
A typical content delivery network does not host content and also cannot replace the requirement of a typical web hosting server. It does, however, help cache content at the network edge. This in turn improves a website’s performance.
A lot of websites often struggle to get their performance needs met through traditional hosting services, and the outcome in this manner is often not desirable. This is the reason they opt for content delivery networks (CDNs).
Through proper utilization of caching to reduce web hosting bandwidth, which help in preventing interruptions in service as well as improving online security;
content delivery networks have become a popular choice that are instrumental in relieving some stress that often arise when using traditional methods of web hosting.
The benefits of using a content delivery network – what are they?
The benefits of a CDNs usage often differ on the size and needs of an internet property, the primary benefits for most users can be segregate into four different components:
- Improving a website’s load times: Through distribution of content closer to website visitors by using a CDN server near them, website visitors experience fast loading times for their websites. Other optimizations are use as well.
- As visitors often click away from a slow loading website, CDns help reduce bounce rates and raise the amount of time visitors spend on a particular website. Faster websites help visitors stick around longer.
- Reduction of bandwidth expenses: A website’s bandwidth cost is a primary expense for it. By means of caching and other needed optimizations, CDNs are able to cut down the amount of data an origin server should give, which in turn reduces costs for website owners.
- Raising content availability and reducing its redundancy: Hardware failures or large amounts of website traffic can hurt a normal website’s working. CDNs are distribute which means they can handle traffic, can compensate for hardware breakdown and can withstand hardware failure easily.
- Improvements in a website’s security: A content delivery network can improve a website’s security through provision of top-of-the-line DDoS mitigation service. Moreover, it can also provide improvements to security certificates and other needed optimizations.
Understanding the modus operandi of a content delivery network – how does it work?
At its very base, a content delivery network (as mentioned earlier) is a network of servers linked together with the main objective of delivery content in a fast, reliable, affordable, accurate, timely and secure manner, in the best possible manner.
To improve speed and connectivity of a website, a CDN will place servers at exchange points between various networks, which also in turn provides content right on time securely. This is a fact verified by experts working at a DDoS Protection Service agency in North York.
The internet exchange points are basically primary locations where various internet service providers connect to provide each other access to traffic originating on various networks (especially their own).
Through the presence of a connection to these high speed and well interconnected locations,
a provider of a CDN is thus able to cut down costs and transit times in terms of delivering high speed data.
Other than the placement of internet exchange points, a content delivery network also makes a number of optimizations on the usual client end and server end data transfers.
These CDNs place data centers at locations that are strategic across the globe, ensuring enhanced security. Moreover, they are created in a way that helps them endure internet congestion and other failures.